Despite guideline suggestions, many sufferers discontinue P2Y12 inhibitor remedy sooner than the really helpful 1 12 months after myocardial infarction (MI), and higher-potency P2Y12 inhibitors are underutilized. Cost is ceaselessly cited as a proof for each of these observations.
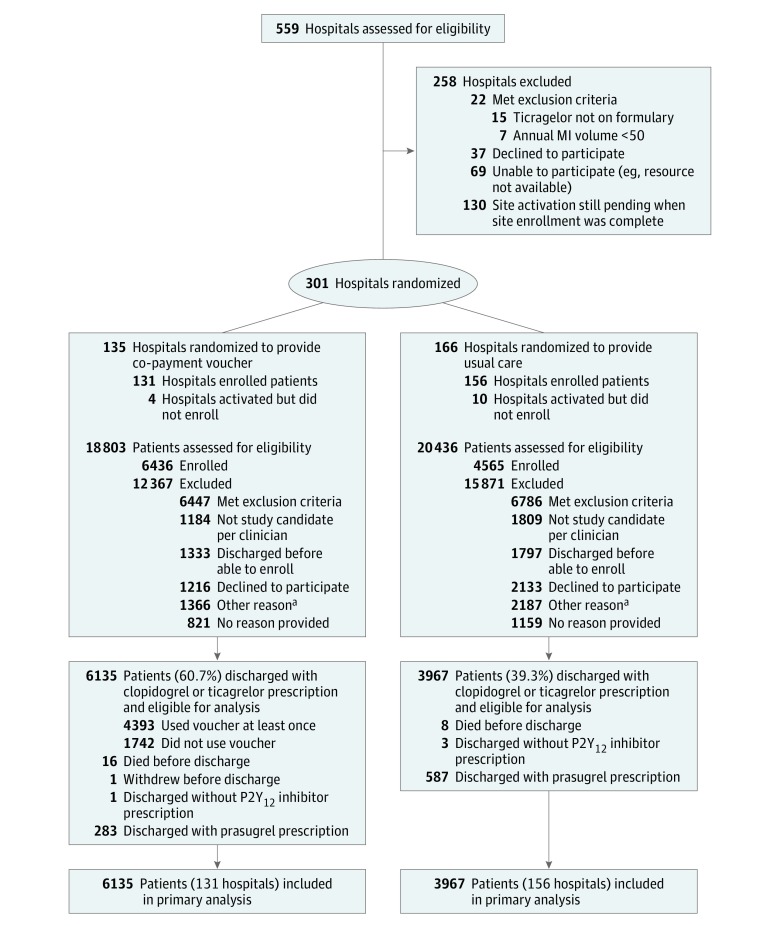
To decide whether or not eradicating co-payment boundaries will increase P2Y12 inhibitor persistence and lowers threat of main opposed cardiovascular occasions (MACE).Cluster randomized medical trial amongst 301 hospitals enrolling grownup sufferers with acute MI (June 5, 2015, by September 30, 2016); sufferers had been adopted up for 1 12 months after discharge (remaining date of follow-up was October 23, 2017), with blinded adjudication of MACE; alternative of P2Y12 inhibitor was per clinician discretion.
Hospitals randomized to the intervention (n = 131 [6436 patients]) offered sufferers with co-payment vouchers for clopidogrel or ticagrelor for 1 12 months (median voucher worth for a 30-day provide, $137 [25th-75th percentile, $20-$339]). Hospitals randomized to regular care (n = 156 [4565 patients]) didn’t present examine vouchers.Independent coprimary outcomes had been patient-reported persistence with P2Y12 inhibitor (outlined as continued therapy with out hole in use ≥30 days) and MACE (loss of life, recurrent MI, or stroke) at 1 12 months amongst sufferers discharged with a prescription for clopidogrel or ticagrelor.Among 11 001 enrolled sufferers (median age, 62 years; 3459 [31%] ladies), 10 102 sufferers had been discharged with prescriptions for clopidogrel or ticagrelor (clopidogrel prescribed to 2317 [36.0%] within the intervention group and 2497 [54.7%] within the regular care group), 4393 of 6135 sufferers (72%) within the intervention group used the voucher, and follow-up information at 1 12 months had been obtainable for 10 802 sufferers (98.2%).
Patient-reported persistence with P2Y12 inhibitors at 1 12 months was increased within the intervention group than within the management group (unadjusted charges, 5340/6135 [87.0%] vs 3324/3967 [83.8%], respectively; P < .001; adjusted distinction, 2.3% [95% CI, 0.4% to 4.1%]; adjusted odds ratio, 1.19 [95% CI, 1.02 to 1.40]).
There was no important distinction in MACE at 1 12 months between intervention and regular care teams (unadjusted cumulative incidence, 10.2% vs 10.6%; P = .65; adjusted distinction, 0.66% [95% CI, -0.73% to 2.06%]; adjusted hazard ratio, 1.07 [95% CI, 0.93 to 1.25]).
Among sufferers with MI, provision of vouchers to offset treatment co-payments for P2Y12 inhibitors, in contrast with no vouchers, resulted in a 3.3% absolute improve in patient-reported persistence with P2Y12 inhibitors and no important discount in 1-year MACE outcomes.ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02406677.

DNA replication stress triggers fast DNA replication fork breakage by Artemis and XPF.
DNA replication stress (DRS) results in the buildup of stalled DNA replication forks leaving a fraction of genomic loci incompletely replicated, a supply of chromosomal rearrangements throughout their partition in mitosis.
MUS81 is understood to restrict the incidence of chromosomal instability by processing these unresolved loci throughout mitosis. Here, we unveil that the endonucleases ARTEMIS and XPF-ERCC1 may also induce stalled DNA replication forks cleavage by non-epistatic pathways all alongside S and G2 phases of the cell cycle.
We additionally confirmed that each nucleases are recruited to chromatin to advertise replication fork restart. Finally, we discovered that fast chromosomal breakage managed by ARTEMIS and XPF is necessary to forestall mitotic segregation defects.
Collectively, these outcomes reveal that Rapid Replication Fork Breakage (RRFB) mediated by ARTEMIS and XPF in response to DRS contributes to DNA replication effectivity and restrict chromosomal instability.
